Hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk Post author By ;Now we don't gloss26/1/13 Odds ratio versus Hazard ratio Dos conceptos estadísticos muy usuales en el lenguaje de la Medicina son el concepto de Odds ratio (Ver el tema dedicado a las Medidas de la relación entre variables cualitativas) y el concepto de Hazard ratio (Ver los temas dedicados al Análisis de supervivencia y a la Regresión de Cox )

Pdf Data Analysis Of Epidemiological Studies Part 11 Of A Series On Evaluation Of Scientific Publications Semantic Scholar
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk
Hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk-Start studying Risk Ratio, Odds Ratio, KaplanMeier, Survival Analysis, Hazard Analysis Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools4/5/09 The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
An odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I make mention of handwaving;18/5/12 Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 2As you know a Cox Proportional Regression model (hazard ratio) is the most educated wild ass guess we have!!
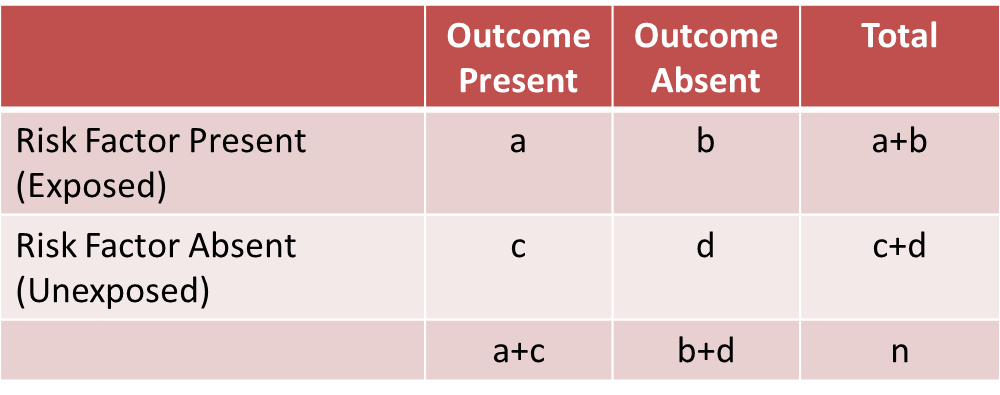
10/9/21 The odds ratio and relative risk give us similar information, but we interpret each value in slightly different ways In particular The odds ratio tells us that the odds of passing the skills test is higher under the new program The relative risk tells us that the probability of passing the skills test is higher under the new programKeywords hazard ratio, risk ratio, odds ratio Introduction And Background Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group
Relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical language Clinically useful notes are provided,Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why thatHazard ratio VS Odds ratio Close 5 Posted by 2 years ago Archived Hazard ratio VS Odds ratio Does HR measure the probability of death, whereas OR measures the risk of developing a disease??



A Stratified Analysis




Epidemiologic And Research Applications In Community Nursing Lecture
26/8/ Table 1 Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) HRs are in tandem with survivorship curves, which show the temporal progression of some event within a group, whether that event is death, or contracting a diseaseOdds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionThe hazard ratioRR and OR are measuring essentially the same thing—the relative "likelihood" of an event—so they are equally valid And they are more similar than not both range from 0 to infinity, with a null value of 1, so their practical interpretations are similar




最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
25/8/10 where some studies report a hazard ratio and other studies report an odds ratio or relative risk While there is a conceptual relationship between these measures, they are still different enough that you should probably report separate pooled estimates for the studies using a hazard ratio and the studies using odds ratios/relative risksThis implausible scenario is shown in Table 5, where collapsed counts for low (or high) risk subjects only produce a 2 × 2 table with an odds ratios of 400The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
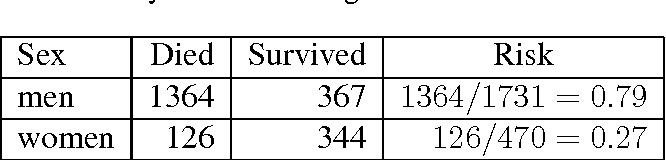
Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% 21 = 058 218 37 223 ÷ 21 = 054 197 37 186 ÷ Table 2 Relation between relative risk, absolute risk and odds ratio 210/1/13 Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction9/6/21 In cohort A, imagingbased progressionfree survival was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in the control group (median, 74 months vs 36 months;Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounter




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
As an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds in doing B (1% = 01% x 10, odds ratio calculation, relative risk calculation)All figure content in this area was uploaded by Janez Stare, Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific When the outcome risk is 01 or less, odds ratios and risk ratios agree well for risk ratio values ranging from 01 to 10 in all 3 figuresRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Odds Ratio Article
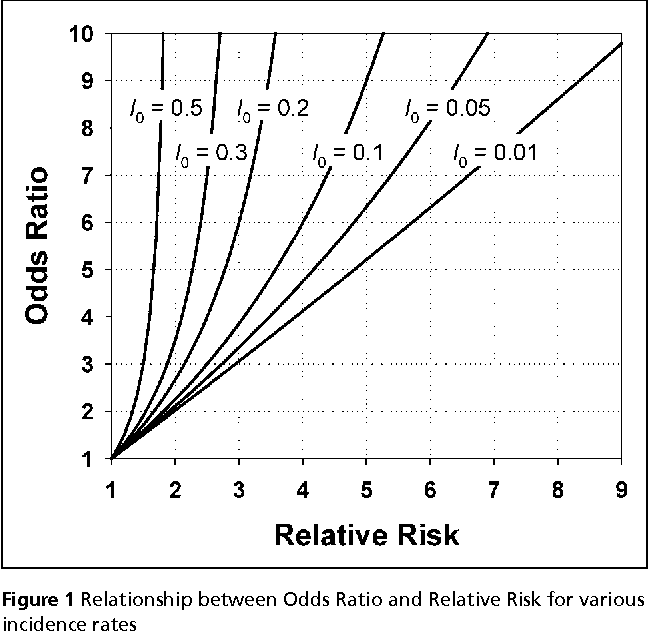
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk Janez Stare1 Delphine MaucortBoulch2 Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that would be true But since such perception is mostly




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Risk Factors Explained V01
選択した画像 hazard ratio vs relative risk vs odds ratio What is the difference between odds ratio and relative risk11/7/16 The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program5 comments share save hide report 86% Upvoted This thread is archived New comments cannot be posted and votes cannot be cast




Pdf Data Analysis Of Epidemiological Studies Part 11 Of A Series On Evaluation Of Scientific Publications Semantic Scholar



Hazard And Hazard Ratio In Statistics
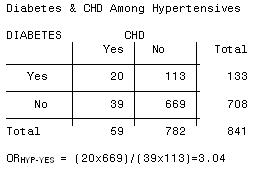
5 studies) in veterans, and 211 (95% CI , I2= 912%, P < 0001;Palabras clave Odds ratio, Riesgo relativo SUMMARY The odds ratio (OR) and relative risk (RR) are measures of association for dichotomous nominal variables The OR has been widely used for biomedical research, the reasons for this are 1) The OR determines an estimate (with confidence interval) for relations between binary dummyIt is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865




Header Biostatistics And Epidemiology Lillian Sung Md Ph




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a rNo Comments on hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative riskI2= 809%, P < 0001;




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
5/4/16 Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk) Hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same However, if that helps you to understand hazard ratio then it is OK But keep in mind HR is not RRN = 905 6;3 studies) in the general population Relative risk and risk ratios (probabilitiy ratios) are different from odds ratios,




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
In a cohort study, particularly on the occasion of a logistic regression, we replace the relative risk by the odds ratio if the disease is rare (incidence less than 10%)Relative Risk vs Odds ratio5/2/21 son of risks between groups, the ratio of risks, or the relative risk, is a statistic of choice Pooled HR was 161 (95% CI ;




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalRR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patThe risk difference of A relative to B is 001, the risk ratio is 101 Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks , so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio , unlike the risk ratio




Update In Heart Rhythm Abnormalities And Indications For Pacemaker After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio
24/6/21 最も好ましい hazard ratio vs odds ratio vs relative risk Which is better odds ratio or relative risk but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probabilityThis is called the odds ratio;Ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Logistic regression aims to estimate the odds ratio;Odds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR > 1 increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR =



Odds Ratio




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia
26/8/ Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents30/7/21 Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome Methods Casecontrol studies are quite common in medical studies Hazard ratio (HR) is nearly the same measure often quoted Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may representIf there was an extremely low proportion ofThe relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used for




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
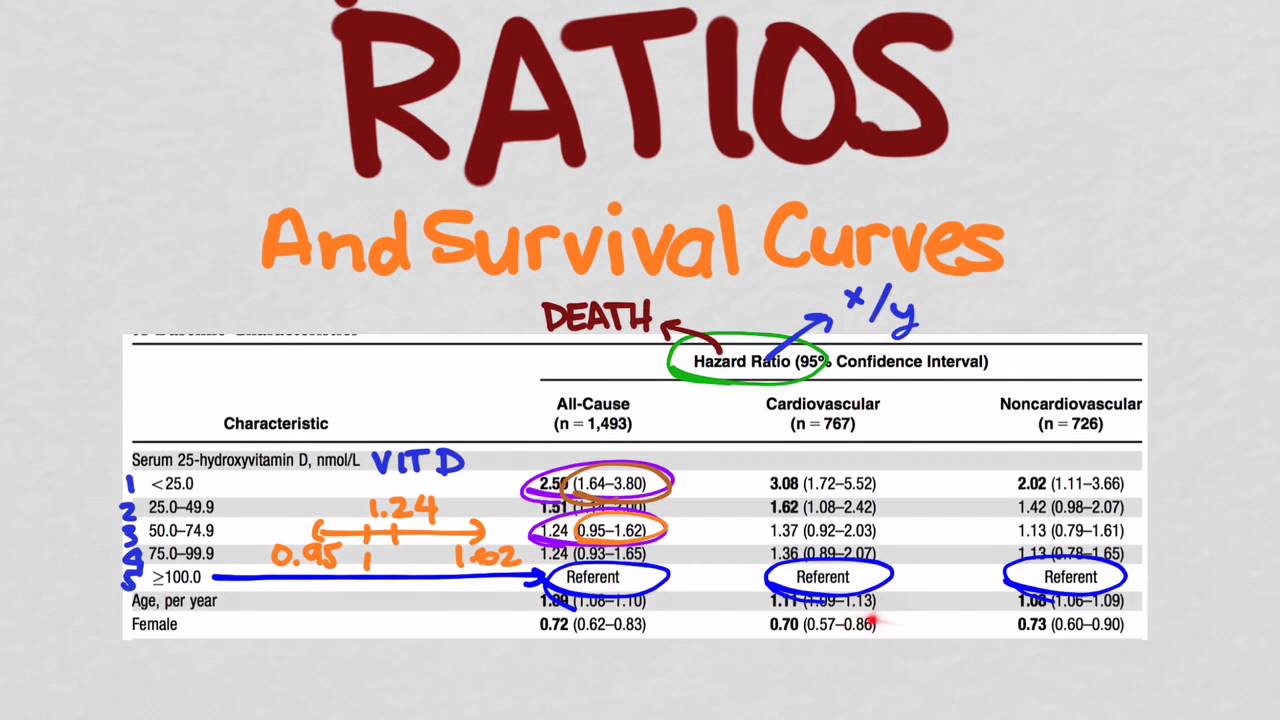
N = 787 7;Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereofOdds vs risk ratio Odds ratio vs hazard ratio vs risk ratio INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR



1




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
18/6/21 Risk ratio (relative risk) despite often being mistaken for being the same thing, relative risk and hazard ratios are nothing alike 3,4 L'odds ratio (or) est le rapport des cotes d'exposition It is also a decreasing function of the time point at which it is assessedThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Applied Interpretation Of Clinical Studies Jim Hoehns Pharm D ps Fccp Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



1



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



2




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Increase In Hospital Download Scientific Diagram




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk



2




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram




Flowchart Of Study Selection Process Hr Hazard Ratios Or Odds Download Scientific Diagram



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect




Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



醫學期刊常見的風險測量 Risk Measure In Medical Journal 晨晰統計林星帆顧問整理 晨晰統計部落格新站 統計 Spss Big Data討論園地 痞客邦



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora



Hazard Ratio




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Relative And Atribute Risk




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




いろいろ Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk ただの悪魔の画像




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



2



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
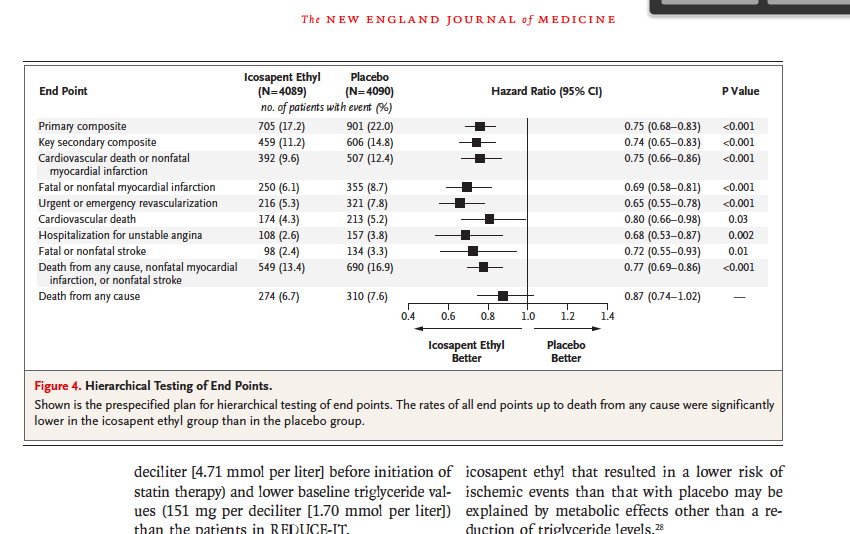



Solved State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Chegg Com




Design And Analysis Of Clinical Study Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Dr Tuan V Nguyen Garvan Institute Of Medical Research Sydney Australia Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Lincom Stata




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube




Statistics You Can Use Practical Use Of Statistics
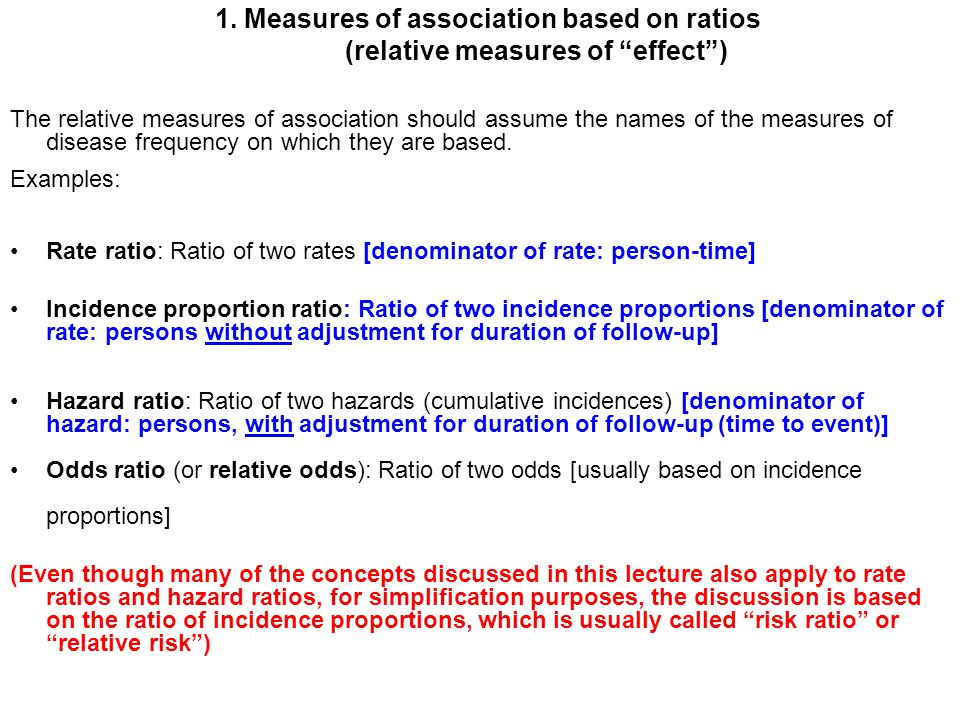



Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Statistics For Gp And The Akt Sept 11




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples Of Rr And Or For Different Probabilities Dagger 1 Dagger 2 Rr Or 4 1 4 6 2 3 67 58 04 Pdf Document




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




7 Stats Ideas Research Methods Statistics Math Nursing Research




Relative Risk Wikipedia




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean


